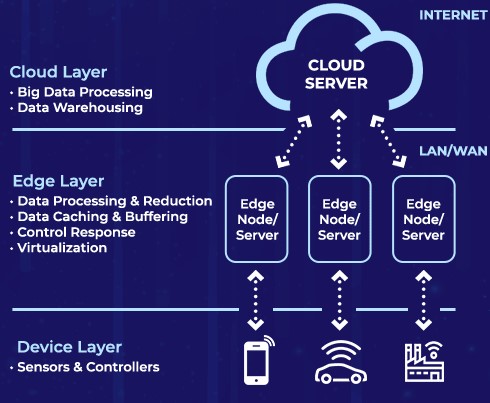
Edge computing & cloud computing are easily two of the significant technological innovations in the past few decades. They have capacitated various industries & domains to reimagine their business. Edge & Cloud computing has fundamentally distinct concepts and characteristics that address different areas.
Here is a detailed comparison table for edge and cloud computing that will help you understand what their core concept is, how they differ, benefits, challenges, and most importantly, use cases – where they work best.
Difference between Edge Computing & Cloud Computing
| Factors | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing | ||||
Concept
|
Edge computing is a distributed computational framework where computation and storage happen at or near the data source itself. | Cloud computing is a concept of storing, managing, and processing data over a network of remote computing infrastructure hosted on the Internet instead of on-premise infrastructure. | ||||
Architecture |
Highly decentralized & distributed computing infrastructure closer to the end devices such as local edge peripherals and IoT devices.
|
Centralized & distributed computing resources hosted in large-scale data centres spread across multiple locations.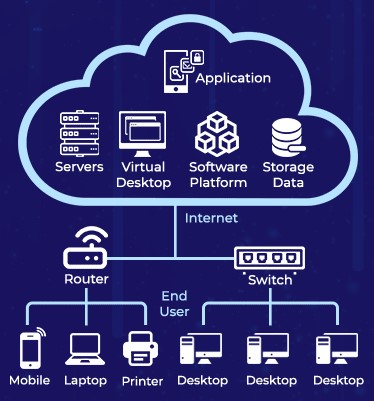 |
||||
Performance |
Edge computing features minimal processing and storage capabilities, focused on latency-critical and real-time analysis. | Cloud computing features powerful computing and enormous storage capabilities, focused on non-time-sensitive, in-depth, and long-term analysis. | ||||
Latency |
|
|||||
Reliability |
Edge computing lacks efficient failover management due to its decentralized nature, Making business continuity uncertain. One significant advantage is that the essential functions rely on the Local Area Network so that it can run operations without an internet connection. |
Cloud computing offers better reliability due to centralized architecture. Data backup and disaster recoveries are possible and relatively easy since systems can be replicated effortlessly. Internet connectivity is crucial; the entire operation may stand a standstill if it fails. |
||||
Scalability |
In edge computing, Scalability is cumbersome because of its highly distributed and dynamic usage environment. | Cloud computing allows for a wide range of computation, network, and storage options for scalability.The provisioning is also easy and quick. | ||||
Security & Compliance |
Edge computing possesses a modest security posture as it can’t withstand sophisticated cyber threats due to its limited processing capabilities. In edge computing, compliances can be met better since most data resides in the local network & storage. |
Cloud computing has a better cybersecurity posture as cloud vendors serve advanced firewalls, access policies, and data protection. In cloud computing, Compliances could be subjective since data resides outside of the local network & storage. |
||||
Technologies |
|
|
||||
Benefits |
|
|
||||
Challenges |
|
|
||||
Use-cases |
|
|
||||
Is this a helpful comparison? Download the interactive infographic on this comparison and share it with your network.