Warehouse operations have undergone a remarkable transformation with noteworthy technological advancements catering to the dynamics of the businesses that produce, distribute, and market goods. In the early 1900s, simple conveyor belts revolutionized the movement of goods in warehouses, making the movement of goods more efficient. The current outlook? Unmatched innovations powered by computing platforms, artificial intelligence, and robots turn warehouses into well-automated playgrounds. Robotic arms, automated storage systems, and self-driving vehicles are prominent warehouse automation technologies.
So, what fuelled this incredible progress?
The explosion of omnichannel commerce played a major role here. With customers demanding seamless product discovery and product delivery, warehouses have updated their operations to realize swift order fulfillment. In addition, the globalization of supply chains has introduced new complexities to warehouse management, leaving businesses searching for smarter solutions to stay competitive and relevant. To tackle these challenges, warehouse automation has evolved as a comprehensive solution that can effectively address the complexities of modern supply chains.
This article delves into warehouse automation, covering its definition, functionality, advantages, available warehouse automation solutions, and role in optimizing warehouse processes.
What is Warehouse Automation?
Warehouse automation is the process of implementing automated systems and technologies to streamline warehouse operations with minimal human intervention.
By incorporating automation, warehouses can optimize inventory management, improve order accuracy, enhance product traceability, and increase efficiency. This means businesses can efficiently manage inventories across multiple locations, ensure smooth order fulfillment, and guarantee accurate and timely deliveries to customers worldwide. It can be achieved through different warehouse automation solutions, which we will see in the following sections.

When we talk about warehouse automation, there are two types: Digital Warehouse Automation and Physical Warehouse Automation.
So, digital warehouse automation is all about using smart software and electronics to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Picture this: A warehouse staff strolling through aisles of the warehouse, casually tapping away on a tablet to know the whereabouts of the SKUs and getting things done. That’s digital automation at work, cutting down on the manual tasks and letting technology do the heavy lifting.
Take Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), for example. They are like the brains of the operation, keeping track of inventory without anyone breaking a sweat. Plus, they help businesses provide real-time updates on their orders, a total game-changer for customer service.
Now, onto physical automation. This is where machines like robots to do time-intensive and labor-intensive work.
Imagine a robotic arm effortlessly picking up, loading them on pallets, and moving them around. That’s physical automation, taking the load off human workers and precisely getting things done.
And you know what’s exciting? The future of warehouse automation will be more promising with all these digital and physical innovations being blended. It’s like having the brains and brawn working hand in hand to make warehouses run smoother than ever before.
How does warehouse automation work?
Warehouse automation is a windfall for organizations managing extensive inventory and complex distribution chains.
Imagine a customer ordering a mobile through an online retail store. Let us see a simple illustration of how warehouse automation operates for this use case.
Initially, when the mobile arrives at the warehouse, advanced barcode or RFID technology swiftly scans and logs SKU details in the inventory management system. The mobile is then properly kept in allocated racks using automated systems.
Upon receiving the customer’s order, the warehouse management system (WMS) quickly processes the information, identifying the most effective methods to locate the ordered SKU. Automation systems such as AS/RS or robotic pickers retrieve the mobile from storage, with AMRs or AGVs ensuring seamless movement to the packing area. The mobile is meticulously sorted and packed using automated and hybrid packing machines according to the customer’s specifications.
Further, the automated system seamlessly manages shipping, including generating labels and coordinating with delivery partners. This end-to-end automation optimizes warehouse operations, providing efficiency and superior customer satisfaction.
For instance, Amazon is a perfect example of how a company can benefit from warehouse automation. With over 750,000 robots working alongside their employees to handle repetitive tasks, they focus on customer service. Amazon leverages warehouse automation technologies from decade-old Kiva robots to autonomous mobile robots (AMR), such as Proteus, to handle the incredible daily volume of orders it receives.
Benefits of Warehouse Automation
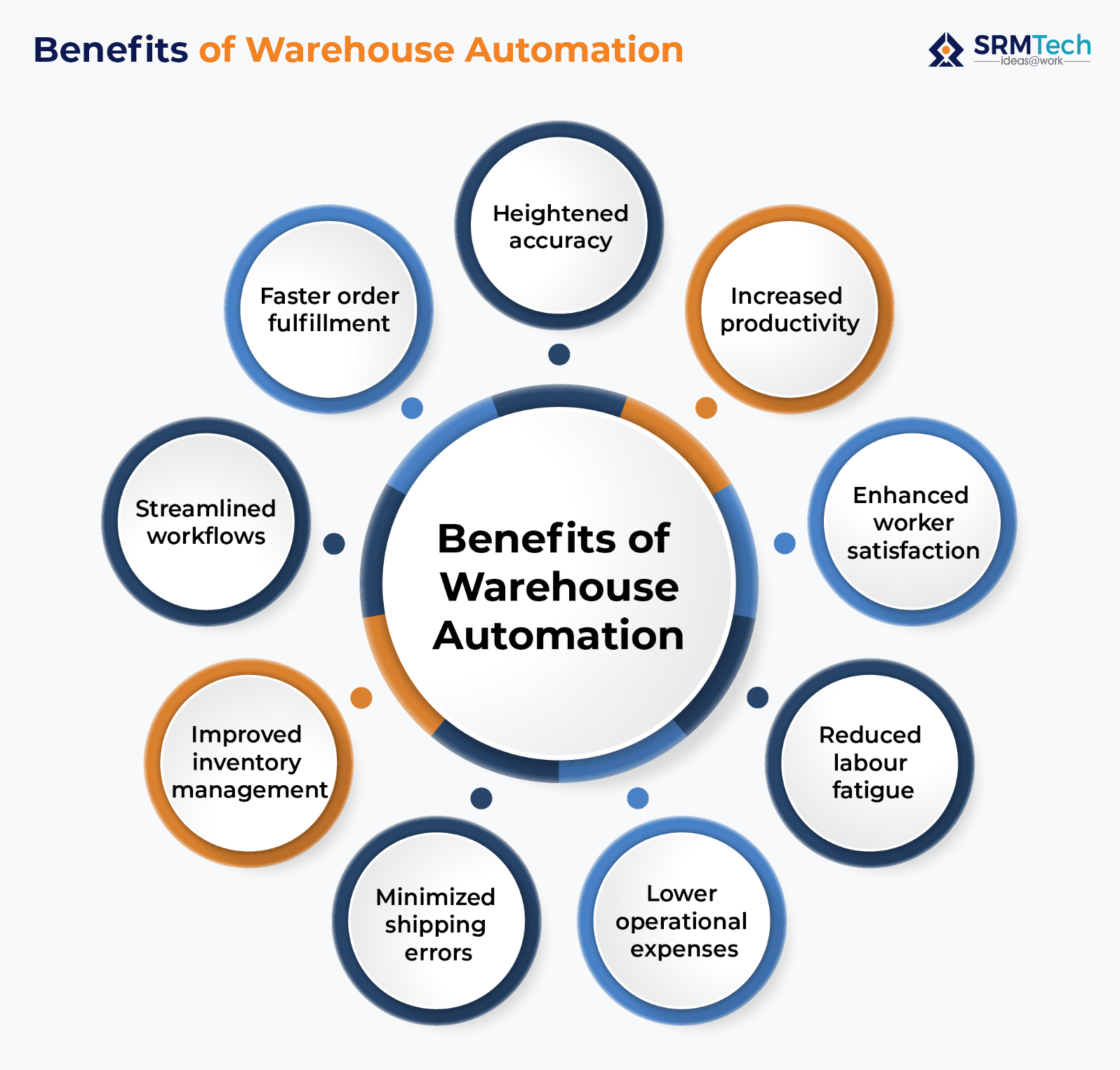
Is it time to automate your warehouse operations? Let’s find out
Deciding whether it’s time to automate your warehouse involves carefully considering various factors. Here are some questions to help guide your decision-making process:
- Are you experiencing capacity constraints or inefficiencies due to manual processes?
- Are order volumes increasing, leading to difficulties meeting customer demands?
- Are you struggling with inventory accuracy and stockouts, or do you have excess inventory levels?
- Are your warehouse staff fatigue becoming a concern, and do you want to enhance their productivity?
- Are you experiencing high error rates in order fulfilment, leading to customer dissatisfaction?
- Are you facing pressure to improve operational efficiency and reduce cycle times?
- Are you looking to scale your operations or expand into new markets?
- Are you seeking to improve visibility and traceability across your supply chain?
- Are you dealing with regulatory compliance requirements that could be better managed through automation?
- Are you experiencing challenges with inefficient inventory data management impeding your ability to make optimal decisions?
If any of the above questions resonate with your current outlook on warehouse operations, it may strongly indicate that it’s time to consider warehouse automation.
How to Automate Your Warehouse
Having a solid plan to start and make your warehouse automation plan efficient and performing to its best is significant. Here are the critical steps for your warehouse automation plan.
Get everyone on board:
Involve all relevant stakeholders, including managers, team leaders, and employees representing your warehouse operation and management. Create a support team and designate project manager(s) to lead the effort.
Gather Management feedback:
Seek input from different levels of management, including corporate leadership and warehouse managers from various locations, to find out the process gaps and inefficiencies in your existing warehouse. Their experiences and insights can provide valuable guidance and help shape your warehouse automation plans.
Assess the risks:
It’s important always to identify potential risks and complexities that may arise during the warehouse automation process. Conduct a risk assessment to understand any obstacles and develop mitigation strategies.
Set goals and deliverables:
Clearly define your goals for warehouse automation. Is it to improve order accuracy, reduce fulfilment time, or streamline inventory management? Identify the specific deliverables you want to achieve and ensure their coverage and possibility with your automation plan.
Choose the right automation solution:
Consider the automation options available in the market. Research different warehouse automation technologies and platforms and request demonstrations to see how they operate. Evaluate which Warehouse automation solutions best align with your specific business goals, customer segment preferences, and operational feedback. Also, consider your available resources in terms of time and budget.
For instance, implementing mobile barcode scanning may have different requirements than installing an AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval System).
Plan and schedule:
The project managers will finally collaborate with the technical team to create a comprehensive schedule. This detailed timeline will highlight key milestones and deliverables, ensuring everyone remains focused and accountable throughout the implementation process.
Remember, warehouse automation is a journey, so communicate with your team and adjust your plans as needed. With a well-thought-out strategy and the right technology, you’ll head to a more efficient and streamlined warehouse operation.
Now that we have explored warehouse automation, its functionality, benefits, and implementation process, let’s dive into the various solutions available for automating warehouse operations.
Warehouse Automation Challenges & Considerations
Overview of Warehouse Automation Technologies
A diverse array of technologies powers automated warehouse management systems, each playing a crucial role in optimizing different aspects of warehouse operations and it is essential to be aware of how they solve warehouse problems while staying current with warehouse technology trends.
- Robotics: Robotics and control systems pick, pack, and transport goods within the warehouse.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): WMS software manages inventory, tracks goods movement, and optimizes real-time warehouse automation operations.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Devices: Sensors, cameras, and devices collect real-time data on inventory levels, temperature, and other parameters, enabling proactive inventory management and monitoring.
- Machine Learning and AI: Algorithms analyze data to optimize processes, forecast demand, and improve decision-making.
- Edge Computing: Processing data near the source reduces latency and improves real-time decision-making, which is crucial for time-sensitive warehouse operations.
- Barcode Scanning: Scanning barcodes on products update inventory records and track their movement efficiently.
- Voice Recognition: Voice commands streamline tasks such as locating items or updating inventory records, enhancing worker productivity.
- Wearable Technology: Smart glasses and RFID-enabled wearables provide real-time data access, improving worker efficiency and order accuracy.
Integration with Warehouse Automation Solutions
The above-mentioned technologies are seamlessly integrated into warehouse automation solutions (both physical and digital) to address specific operational challenges and enhance competence:
Robotics:
Robotics plays a crucial role in warehouse automation, which uses advanced technology to streamline operations. As per Gartner research, 95% of supply chain organizations have invested or plan to invest in robotics automation. Robotic solutions like Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Robotic Arms, and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) are commonly used to transport goods, stack shelves, and pack orders efficiently. These robots are fully equipped with cameras and sensors to navigate the warehouse space safely and accurately.
Let’s look into prominent robotic systems targeting the order fulfillment process.
Autonomous Forklifts
Autonomous forklifts significantly contribute to the development of automated warehouses and fulfillment centers, leading to efficient and high-performing supply chain infrastructure. These driverless robotic forklifts can be programmed and remotely managed by trained professionals to execute predominant material handling tasks like loading, unloading, and pallet movements inside the warehouse. Autonomous forklifts could be a great advantage, especially during heavy lifting and hazardous material handling, thus minimizing human intervention and reducing the risk of accidents. As they are equipped with technologies like machine vision algorithms and LIDAR sensors, these self-driving forklifts can avoid obstacles and accurately navigate the warehouse premises. Warehouse management teams can even achieve real-time monitoring and control of material handling processes by integrating these autonomous forklifts with existing warehouse management systems.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs):
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are indispensable in warehouse automation, which follows fixed paths or routes defined by physical guidance systems like magnetic strips, wires, or laser reflectors embedded in the floor.
They receive instructions regarding the items to be picked or transported from a WMS. AGVs navigate efficiently through the warehouse environment by utilizing their onboard sensors and navigation technology, selecting optimal routes, and avoiding obstacles. Once they reach the designated storage locations, AGVs pick up the item and facilitate order packing by transporting goods to the shipping area, typically operating independently. This streamlines the order fulfilment process, reducing the time required for manual material handling and increasing accuracy.
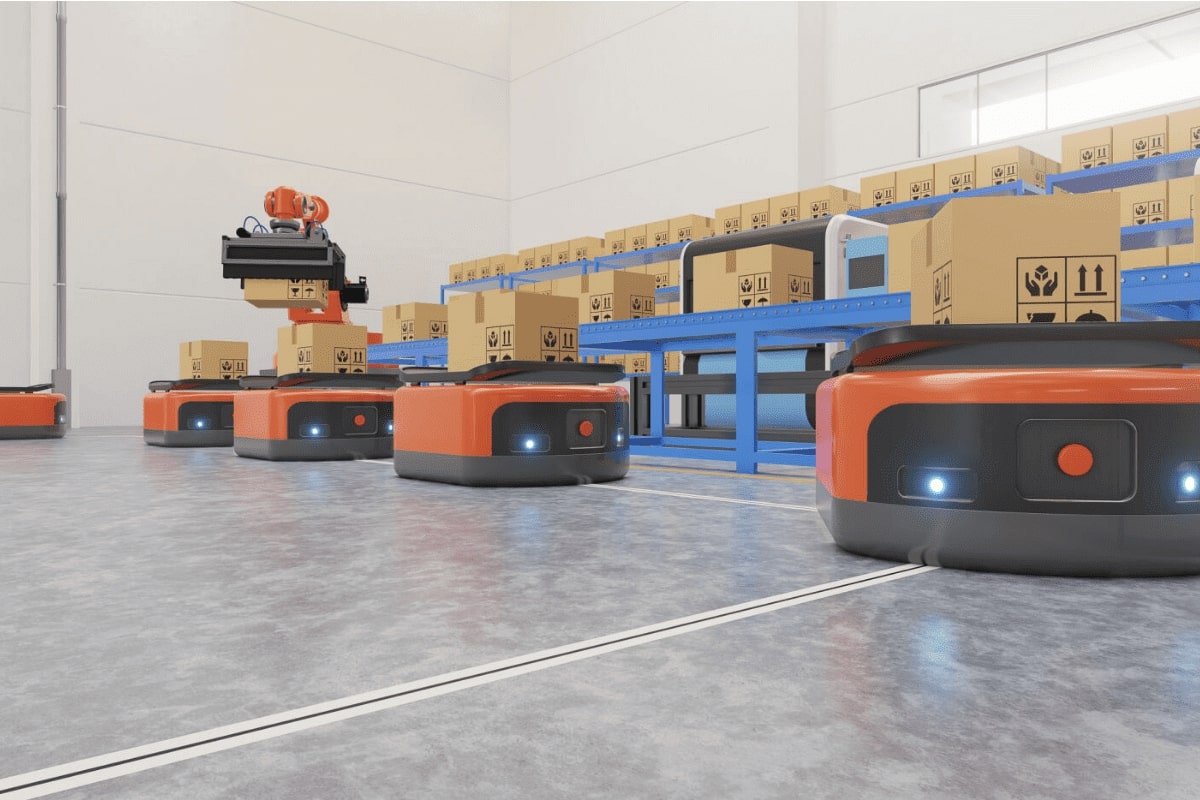

Autonomous Mobile Robots(AMRs)
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are reshaping warehouse automation with their ability to navigate dynamically and adapt to changing environments. Equipped with sensors and onboard computers, AMRs efficiently transport goods within warehouses, seamlessly integrating with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) for tasks like picking and replenishment.
They are designed to work collaboratively with humans and other robots, allowing them to navigate shared spaces safely and efficiently – which means they are one of the types of GTP automation.
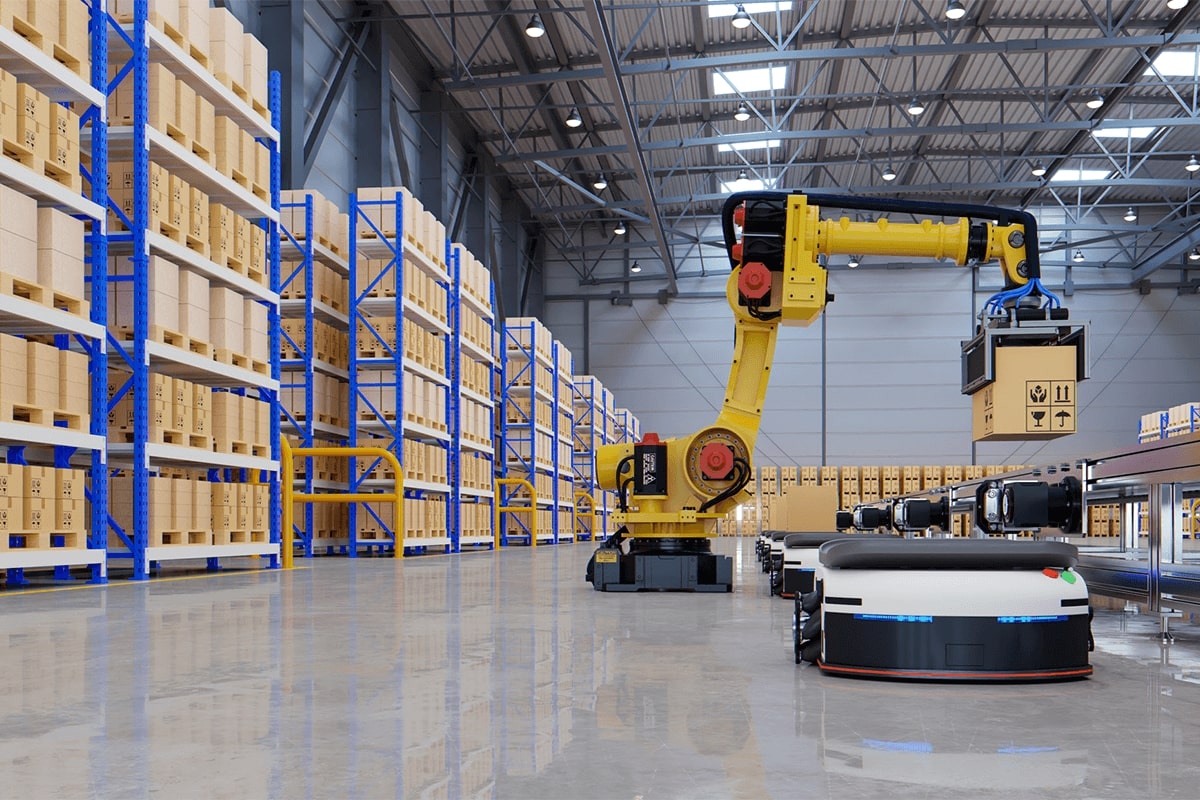

With their versatility and adaptability, AMRs offer a transformative solution for streamlining material handling processes and optimizing warehouse operations.
Goods-to-person (GTP) automation
GTP streamlines warehouse operations by delivering items directly to workers rather than requiring them to navigate aisles. This approach reduces travel time, enhances efficiency, and minimizes labor-intensive tasks. With GTP systems, robots or conveyors transport goods to designated workstations, where employees can fulfill orders rapidly. By eliminating the need for workers to search for items manually, GTP technology improves accuracy and productivity while optimizing space utilization within the warehouse. Overall, GTP solutions enable warehouses to handle higher order volumes, reduce operational costs, and ensure timely order fulfilment to meet customer demands effectively.
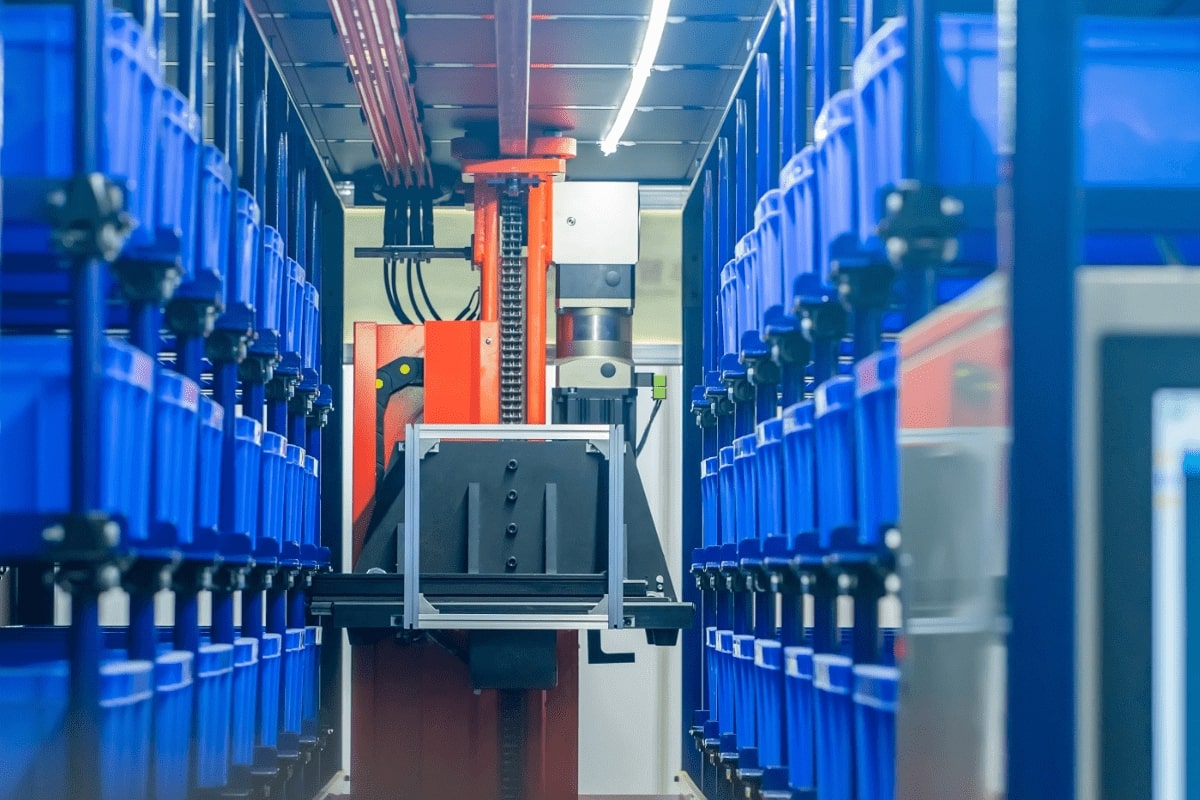

Below are a few types of GTP warehouse automation solutions.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS):
AS/RS refers to various computer-controlled methods that streamline the storage and retrieval of goods in warehouses by automating these tasks. Using robotic arms or shuttles, these systems transport items to and from designated storage locations, maximizing storage density and minimizing labor requirements.
British Sugar used AS/RS to handle 3,000 pallets daily (palate-large trays or platforms to stack and move goods in warehouses). British Sugar’s AS/RS system helped them handle these pallets more efficiently, automatically connecting them to production lines.
Conveyor Belt Systems:
Conveyor belt systems are easily one of the traditional warehouse automation systems, acting as a goods-to-person solution. They efficiently transport items from inventory to workers for processing. By incorporating sensors, barcode scanners, and sorting mechanisms, these systems ensure precise tracking and movement of products along the belts. Integrated with smart software, they optimize routes, monitor inventory levels, and significantly reduce manual labor.
Pick-to-Light:
Pick-to-light is a technology revolutionizing order-picking processes in warehouses and distribution centers. It involves equipping storage locations with display units, typically LED lights or digital screens. When orders are processed, the WMS identifies the SKUs to be picked and their corresponding storage locations. Now, the respective display units from the identified storage location light up, visually guiding pickers to the exact location of the items needed, thereby reducing search time and minimizing errors. Once at the storage location, pickers confirm their picks by pressing a button or triggering a sensor on the display unit. This confirmation updates inventory levels in real-time, ensuring accurate stock information.
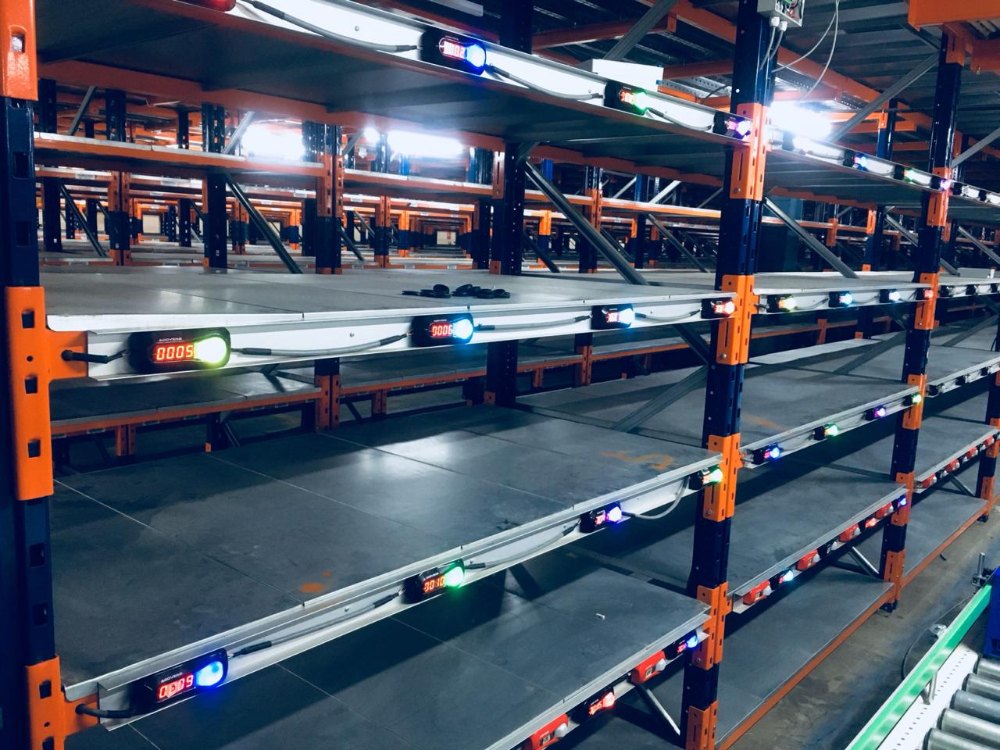

Voice Picking:
Voice-picking technology revolutionizes warehouse automation systems by enabling intuitive guidance for workers during order-picking processes. Utilizing sophisticated voice recognition technology and employing real-time communication and speech synthesis, workers receive instructions and confirm tasks using simple voice commands, which they receive through audio wearables, thus minimizing the inefficiency of manual warehouse chores.

Research and Markets predict that the global voice-picking solutions market will grow at 15.3% annually, reaching $2.9 billion by 2025.
Businesses can adopt any type of warehouse automation technologies and solutions discussed, based on their unique business requirements outlined during the planning phase.
Illustration of How Warehouse Automation Systems Enhances Warehouse Processes with Examples
| No. | Warehouse Process | Example Warehouse Automation Solutions/Technologies | How can it be used? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Product Inventory Management | Wearable technology, Sensors, Automated storage systems |
|
| 2 | Picking & Packing | Goods-to-person systems, Automated dimensioning tools, AGVs |
|
| 3 | Shipping Label Creation | Warehouse Management System (WMS) software |
|
| 4 | Shipping & Receiving | Warehouse Management System (WMS) software |
|
| 5 | Dimensioning | Automated Dimensioning systems |
|
| 6 | Order Fulfillment | Warehouse Management System (WMS) software, Robotics |
|
What Does the Future Hold for Warehouse Automation?
As customer expectations continue to rise, warehouses are compelled to adapt by embracing the latest technological trends for enhanced operations. The future of warehouses lies in automation, driven by AI and big data, with a predicted 50% automation rate by 2030, which is at just 5% now. While automation is crucial, a human touch remains essential for maintaining seamless operations and balancing efficiency with customer satisfaction.
At SRM Tech, we’ve achieved significant milestones in supply chain optimization through thoughtful digitalization and automation solutions, including partnering with a renowned fashion retail giant to transform its supply chain operations till their last-mile delivery. Leveraging our proven expertise and innovative solutions spanning platforms, data, and hardware systems, we drive efficiency, agility, and profitability for our clients across diverse industries by ensuring unparalleled supply chain success. Reach out to us to discover how we can transform your warehouse operations for the future.






